The scales scale_colour_continuous() and scale_fill_continuous() are
the default colour scales ggplot2 uses when continuous data values are
mapped onto the colour or fill aesthetics, respectively. The scales
scale_colour_binned() and scale_fill_binned() are equivalent scale
functions that assign discrete color bins to the continuous values
instead of using a continuous color spectrum.
Usage
scale_colour_continuous(
...,
palette = NULL,
aesthetics = "colour",
guide = "colourbar",
na.value = "grey50",
type = getOption("ggplot2.continuous.colour")
)
scale_fill_continuous(
...,
palette = NULL,
aesthetics = "fill",
guide = "colourbar",
na.value = "grey50",
type = getOption("ggplot2.continuous.fill")
)
scale_colour_binned(
...,
palette = NULL,
aesthetics = "colour",
guide = "coloursteps",
na.value = "grey50",
type = getOption("ggplot2.binned.colour")
)
scale_fill_binned(
...,
palette = NULL,
aesthetics = "fill",
guide = "coloursteps",
na.value = "grey50",
type = getOption("ggplot2.binned.fill")
)Arguments
- ...
Arguments passed on to
continuous_scale,binned_scalenameThe name of the scale. Used as the axis or legend title. If
waiver(), the default, the name of the scale is taken from the first mapping used for that aesthetic. IfNULL, the legend title will be omitted.breaksOne of:
NULLfor no breakswaiver()for the default breaks computed by the transformation objectA numeric vector of positions
A function that takes the limits as input and returns breaks as output (e.g., a function returned by
scales::extended_breaks()). Note that for position scales, limits are provided after scale expansion. Also accepts rlang lambda function notation.
n.breaksAn integer guiding the number of major breaks. The algorithm may choose a slightly different number to ensure nice break labels. Will only have an effect if
breaks = waiver(). UseNULLto use the default number of breaks given by the transformation.labelsOne of the options below. Please note that when
labelsis a vector, it is highly recommended to also set thebreaksargument as a vector to protect against unintended mismatches.NULLfor no labelswaiver()for the default labels computed by the transformation objectA character vector giving labels (must be same length as
breaks)An expression vector (must be the same length as breaks). See ?plotmath for details.
A function that takes the breaks as input and returns labels as output. Also accepts rlang lambda function notation.
limitsOne of:
NULLto use the default scale rangeA numeric vector of length two providing limits of the scale. Use
NAto refer to the existing minimum or maximumA function that accepts the existing (automatic) limits and returns new limits. Also accepts rlang lambda function notation. Note that setting limits on positional scales will remove data outside of the limits. If the purpose is to zoom, use the limit argument in the coordinate system (see
coord_cartesian()).
rescalerA function used to scale the input values to the range [0, 1]. This is always
scales::rescale(), except for diverging and n colour gradients (i.e.,scale_colour_gradient2(),scale_colour_gradientn()). Therescaleris ignored by position scales, which always usescales::rescale(). Also accepts rlang lambda function notation.oobOne of:
Function that handles limits outside of the scale limits (out of bounds). Also accepts rlang lambda function notation.
The default (
scales::censor()) replaces out of bounds values withNA.scales::squish()for squishing out of bounds values into range.scales::squish_infinite()for squishing infinite values into range.
transformFor continuous scales, the name of a transformation object or the object itself. Built-in transformations include "asn", "atanh", "boxcox", "date", "exp", "hms", "identity", "log", "log10", "log1p", "log2", "logit", "modulus", "probability", "probit", "pseudo_log", "reciprocal", "reverse", "sqrt" and "time".
A transformation object bundles together a transform, its inverse, and methods for generating breaks and labels. Transformation objects are defined in the scales package, and are called
transform_<name>. If transformations require arguments, you can call them from the scales package, e.g.scales::transform_boxcox(p = 2). You can create your own transformation withscales::new_transform().positionFor position scales, The position of the axis.
leftorrightfor y axes,toporbottomfor x axes.callThe
callused to construct the scale for reporting messages.superThe super class to use for the constructed scale
nice.breaksLogical. Should breaks be attempted placed at nice values instead of exactly evenly spaced between the limits. If
TRUE(default) the scale will ask the transformation object to create breaks, and this may result in a different number of breaks than requested. Ignored if breaks are given explicitly.rightShould the intervals be closed on the right (
TRUE, default) or should the intervals be closed on the left (FALSE)? 'Closed on the right' means that values at break positions are part of the lower bin (open on the left), whereas they are part of the upper bin when intervals are closed on the left (open on the right).show.limitsshould the limits of the scale appear as ticks
- palette
One of the following:
NULLfor the default palette stored in the theme.a character vector of colours.
a single string naming a palette.
a palette function that when called with a numeric vector with values between 0 and 1 returns the corresponding output values.
- aesthetics
The names of the aesthetics that this scale works with.
- guide
A function used to create a guide or its name. See
guides()for more information.- na.value
Missing values will be replaced with this value.
- type
The preferred mechanism for setting the default palette is by using the theme. For example:
theme(palette.colour.discrete = "viridis").
Details
: The mechanism of setting defaults via
options() is superseded by theme settings. The preferred method to change
the default palette of scales is via the theme, for example:
theme(palette.colour.continuous = scales::pal_viridis()). The
ggplot2.continuous.colour and ggplot2.continuous.fill options could be
used to set default continuous scales and ggplot2.binned.colour and
ggplot2.binned.fill options to set default binned scales.
These scale functions are meant to provide simple defaults. If
you want to manually set the colors of a scale, consider using
scale_colour_gradient() or scale_colour_steps().
Color Blindness
Many color palettes derived from RGB combinations (like the "rainbow" color
palette) are not suitable to support all viewers, especially those with
color vision deficiencies. Using viridis type, which is perceptually
uniform in both colour and black-and-white display is an easy option to
ensure good perceptive properties of your visualizations.
The colorspace package offers functionalities
to generate color palettes with good perceptive properties,
to analyse a given color palette, like emulating color blindness,
and to modify a given color palette for better perceptivity.
For more information on color vision deficiencies and suitable color choices see the paper on the colorspace package and references therein.
See also
continuous_scale() and binned_scale()
The documentation on colour aesthetics.
The continuous colour scales section of the online ggplot2 book.
Other colour scales:
scale_alpha(),
scale_colour_brewer(),
scale_colour_discrete(),
scale_colour_gradient(),
scale_colour_grey(),
scale_colour_hue(),
scale_colour_identity(),
scale_colour_manual(),
scale_colour_steps(),
scale_colour_viridis_d()
Examples
# A standard plot
p <- ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy, colour = cty)) +
geom_point()
# You can use the scale to give a palette directly
p + scale_colour_continuous(palette = c("#FEE0D2", "#FC9272", "#DE2D26"))
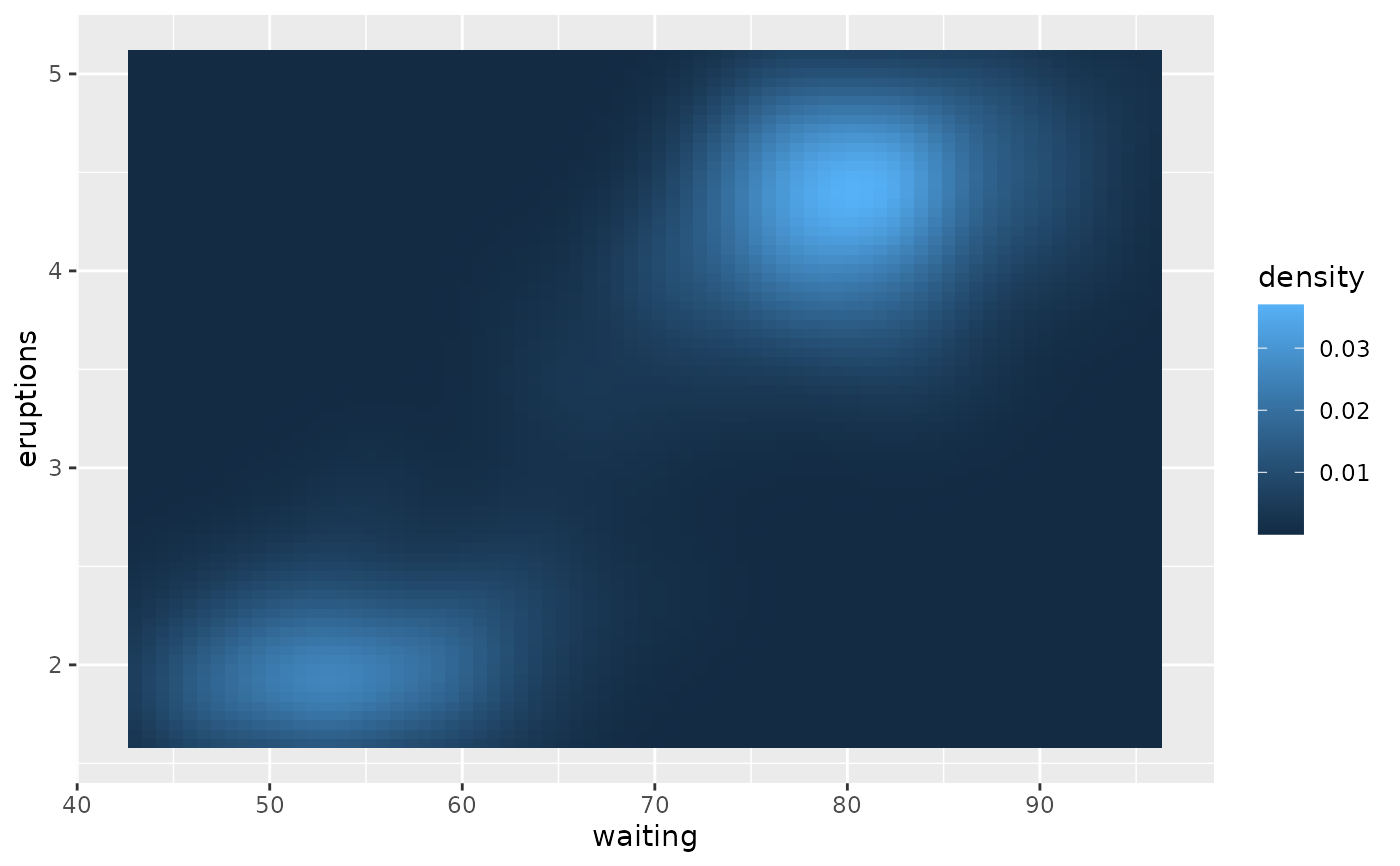 # The default colours are encoded into the theme
p + theme(palette.colour.continuous = c("#DEEBF7", "#9ECAE1", "#3182BD"))
# The default colours are encoded into the theme
p + theme(palette.colour.continuous = c("#DEEBF7", "#9ECAE1", "#3182BD"))
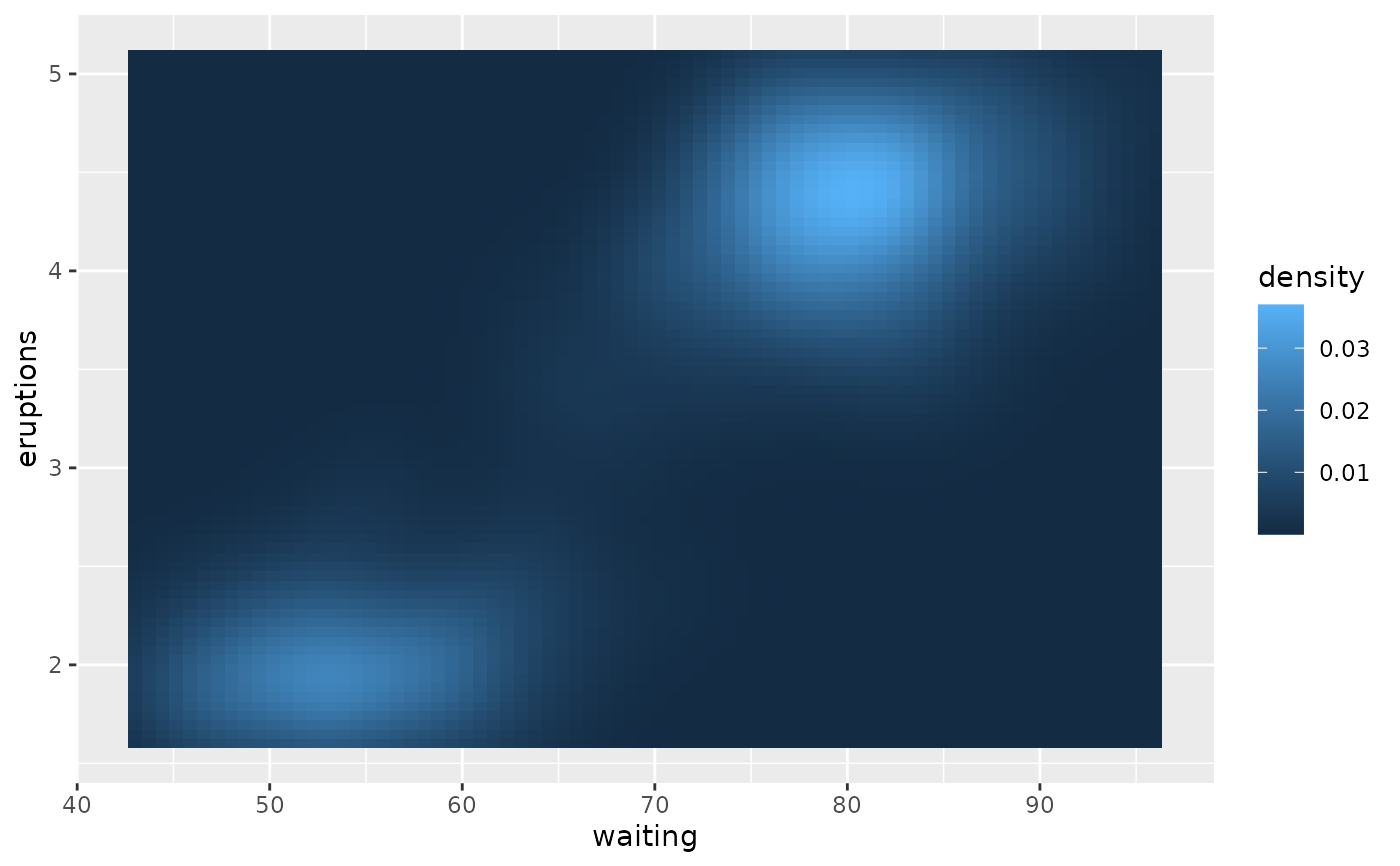 # You can globally set default colour palette via the theme
old <- update_theme(palette.colour.continuous = c("#E5F5E0", "#A1D99B", "#31A354"))
# Plot now shows new global default
p
# You can globally set default colour palette via the theme
old <- update_theme(palette.colour.continuous = c("#E5F5E0", "#A1D99B", "#31A354"))
# Plot now shows new global default
p
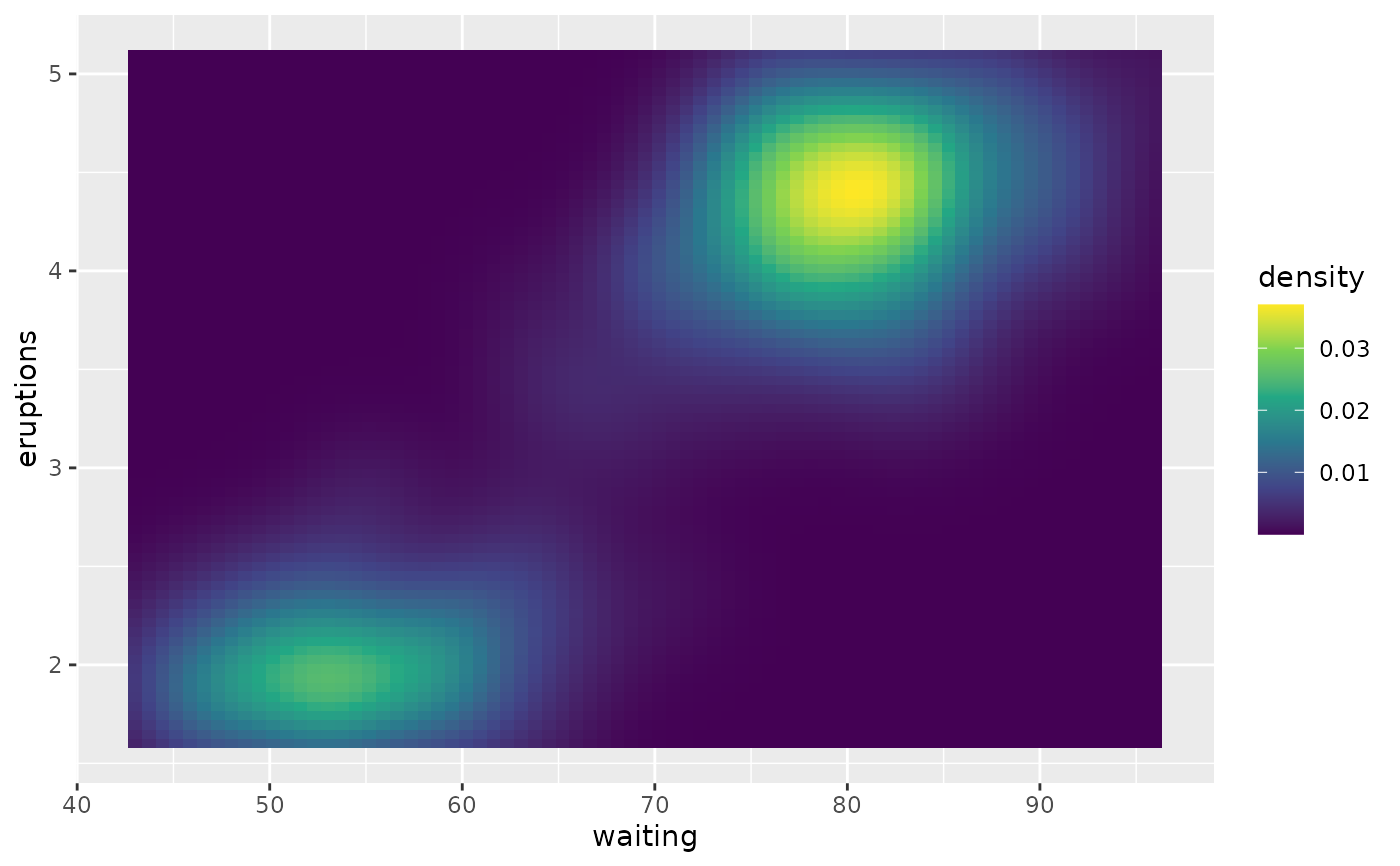 # The default binned colour scale uses the continuous palette
p + scale_colour_binned() +
theme(palette.colour.continuous = c("#EFEDF5", "#BCBDDC", "#756BB1"))
# The default binned colour scale uses the continuous palette
p + scale_colour_binned() +
theme(palette.colour.continuous = c("#EFEDF5", "#BCBDDC", "#756BB1"))
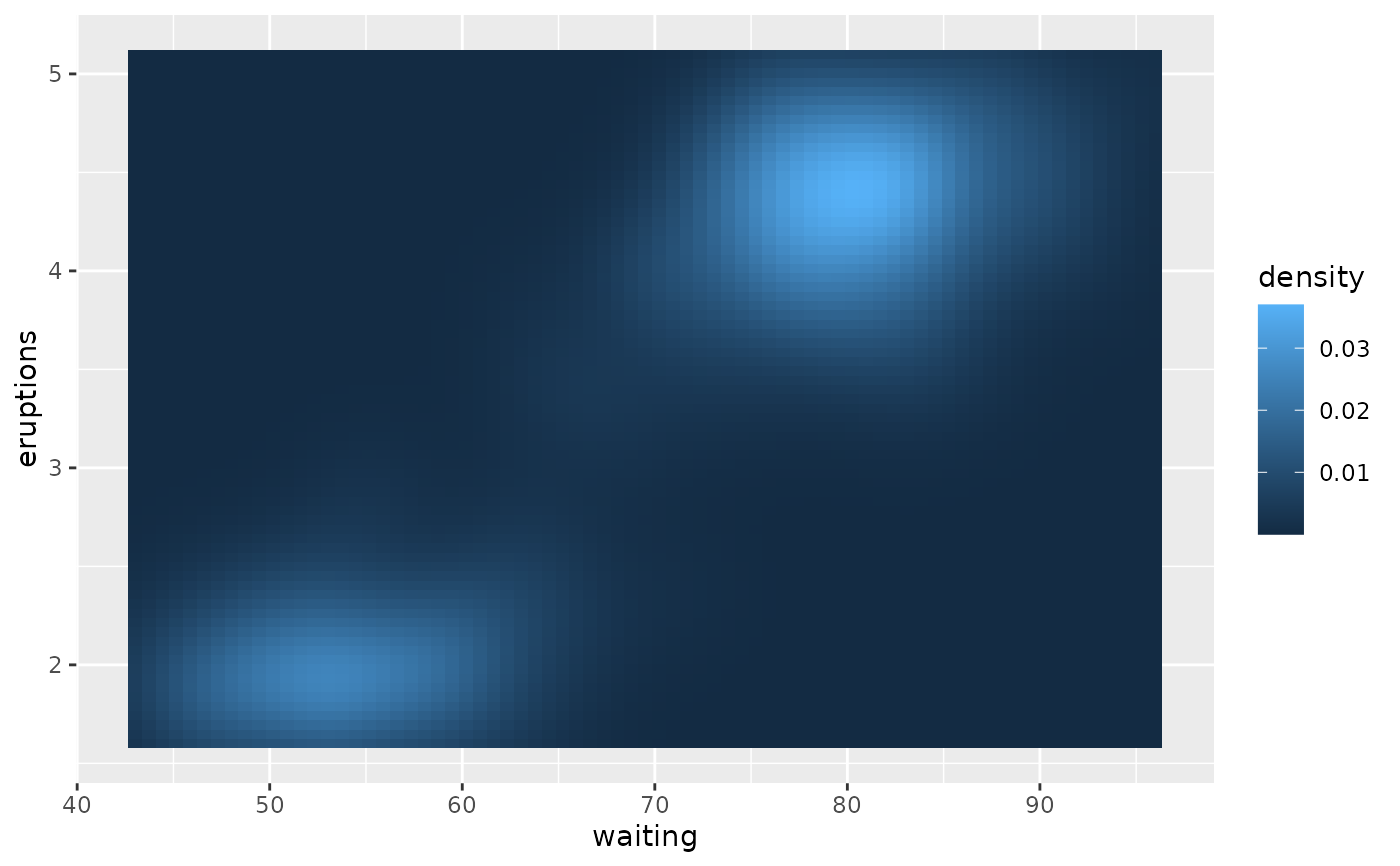 # Restoring the previous theme
theme_set(old)
# Restoring the previous theme
theme_set(old)
